solar energy system and application
Introduction:
Welcome guys today i will give you information about solar energy system and it's application and also type of solar energy system.
SOLAR ENERGY STORAGE AND
APPLICATIONS:
Solar Energy Storage:
• Solar energy is available only during the sunshine hours.
• Consumer energy demands follow their own time pattern and the solar energy
does not fully match the demand. As a result, energy storage is a must to meet the
consumer requirement.
• There are three.
Sensible Heat Storage:
👉Heating a liquid or solid which does not change phase comes under this
category.
👉Heat that causes a change in temperature in an object is called sensible heat.
👉The quantity of heat stored is proportional to the temperature rise of the
material.
👉If T1
and T2
represent the lower and higher temperature, V the volume and ρ
the density of the storage material, and Cp
the specific heat, then the energy stored
Q is given by:
Q= V integration T1to T2 Cp dT
👉For a sensible heat storage system, energy is stored by heating a liquid or a
solid. Materials that are used in such a system include liquids like water, inorganic
molten salts and solids like rock, gravel and refractories.
👉The choice of the material used depends on the temperature level of its
utilization. Water is used for temperature below 100 0C whereas refractory bricks
can be used for temperature upto 1000 C
LATENT HEAT STORAGE (PHASE CHANGE HEAT STORAGE):
👉 All pure substances in nature are able to change their state. Solids can become
liquids (ice to water) and liquids can become gases (water to vapor) but changes
such as these require the addition or removal of heat.
👉 In this system, heat is stored in a material when it melts, and heat is extracted
from the material when it freezes.
👉 Heat can also be stored when a liquid changes to gaseous state, but as the
volume change is large, such a system is not economic.
👉Latent heat arises from the work required to overcome the forces that hold
together atoms or molecules in a material. The regular structure of a crystalline
solid is maintained by forces of attraction among its individual atoms, which
oscillate slightly about their average positions in the crystal lattice.
THERMO-CHEMICAL STORAGE:
👉With a thermo-chemical storage system, solar heat energy can start an
endothermic chemical reaction and new products of reactions remain intact.
👉To extract energy, a reverse exothermic reaction is allowed to take place.
👉 Actually, thermo-chemical thermal energy is the binding energy of reversible
chemical reactions.
STRATIFIED STORAGE:
👉A hot water storage tank (also called a hot water tank, thermal storage tank, hot
water thermal storage unit, heat storage tank and hot water cylinder) is a water
tank used for storing hot water for space heating or domestic use.
👉An efficiently insulated tank can retain stored heat for days.
👉Hot water tanks may have a built-in gas or oil burner system, electric immersion
heaters, an external heat exchanger such as a central heating system, or heated
water from another energy source such as a wood-burning stove.
SOLAR PONDS:
👉Normal ponds receive sunlight a part of which is reflected at the surface, a part is absorbed and the
remaining is transmitted to the bottom.
👉Due to this the lower part gets heated up and the density decreases as a result of which it rises up and
convection currents are set up.(As a result, the heated water reaches top layer and looses its heat by
convection and evaporation).
👉A natural or artificial body of water for collecting and absorbing solar radiation energy and storing it
as heat.
👉Thus a solar pond combines solar energy collection and sensible heat storage.
👉They are large shallow bodies of water that are arranged so that the temperature gradient are reversed
from the normal.
👉This allows the use for collection and storage of solar energy which may under ideal conditions be
delivered at temperature 40-50 `C above normal.
👉It can be use for various applications, such as process heating, water desalination, refrigeration,
drying and power generation.
UPPER CONVECTIVE ZONE-
This is a zone, typically 3 m thick, of almost low salinity which is almost close to
ambient temperature.
NON CONVECTING ZONE-
In this zone both salinity and temperature increases with depth.
LOWER CONVECTING ZONE-
relatively high salinity ( typically 20 % by weight) at high temperature.
Solar Distillation:
👉Solar distillation is the use of solar energy to evaporate water and
collect its condensate within the same closed system.
👉water purification it can turn salt or brackish water into fresh drinking
water.
Solar Drying:
• Solar dryers are devices that use solar energy to dry the substances
especially food.
• There are two general types of solar dryers
👉direct dryer
👉Indirect dryer
PHOTOVOLTAIC ENERGY CONVERSION:
👉Photovoltaic systems convert sunlight directly into electricity, and are
potentially one of the most useful of the renewable energy technologies.
👉Also known as solar cells, PV systems are already an important part of
our lives. The simplest systems power many of the small calculators and
wrist watches we use everyday.
👉The conversion efficiency of a PV cell is the proportion of sunlight
energy that the cell converts into electrical energy.
👉A solar cell is essentially a semiconductor device fabricated in a manner
which generates a voltage when solar radiation falls on it.
👉Solar electricity systems capture the sun's energy using photovoltaic
(PV) cells.
👉The cells convert the sunlight into electricity, which can be used to run
household appliances and lighting.
👉A SOLAR CELL is a solid state electrical device that converts energy of
light directly into electricity by Photoelectric Effect.
PHOTOELECTRIC EFFECT:
👉When photons of light hit electrons in the silicon lattice and provide
energy to flow. Introducing dopants such as boron and phosphorus into
the silicon lattice provides a direction for the electrons to flow.
👉Finally, electrons flowing from one cell into the next cell in a module
gain about 1/2 volt from each cell.
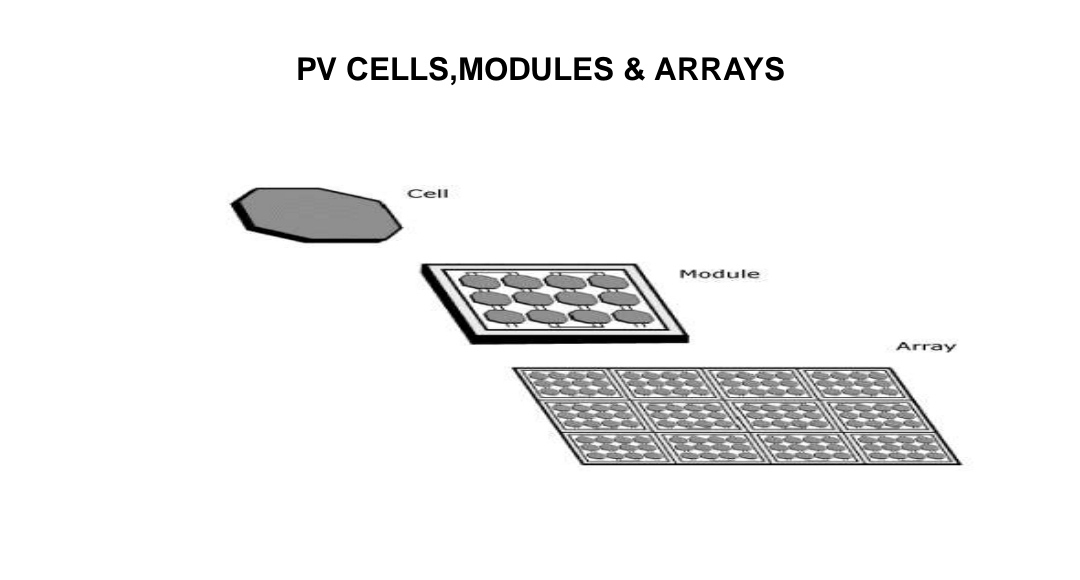
A PV System typically consists of 3 basic components:
👉PV cells - Electricity is generated by PV cells, the smallest unit of a PV system.
👉Modules - PV cells are wired together to form modules which are usually a
sealed, or encapsulated, unit of convenient size for handling.
👉Arrays – Groups of panels make up an array.
👉Solar cells are fixed on a board and connected in series and parallel
combinations to provide the required voltage and power to form a
photovoltaic (PV) module.
👉To protect the cells from damage the module is hermetically sealed
between a plate of toughened glass and layers of Ethyl Vinyl Acetate.
👉A terminal box is attached to the back of module where the two ends of
solar string are shouldered to the terminals.
👉When the PV module is in use, terminals are connected directly to the
load.
PV CELL WORKING PRINCIPLE:
👉Photovoltaic cells are made of special materials called semiconductors such as
silicon. An atom of silicon has 14 electrons, arranged in three different shells. The
outer shell has 4 electrons.
👉Therefore a silicon atom will always look for ways to fill up its last shell, and to
do this, it will share electrons with four nearby atoms.
👉Now we use phosphorus(with 5 electrons in its outer shell). Therefore when it
combines with silicon, one electron remains free.
👉A PV module produces DC power. To operate electrical appliances used in
households, inverters are used to convert DC power into 220 V, 50 Hz AC power.
Components other than PV modules are collectively known as balance of system
(BOS) which includes storage batteries, an electronic charge controller and an
inverter.
👉When sunlight strikes solar cell surface, the cell creates charge carrier as electrons
and holes. The internal field produced by junction separates some of positive
charges (holes) from negative charges (electrons). Holes are swept into positive or
p-layer and electrons are swept into negative or n-layer.
👉When a circuit is made, free electrons have to pass through the load to recombine
with positive holes; current can be produced from the cells under illumination.
COMPONENTS OF SOLAR PV SYSTEM:
👉Solar Module is the essential component of any solar PV system that converts
sunlight directly into DC electricity.
👉Solar Charge Controller regulates voltage and current from solar arrays, charges
the battery, prevents battery from overcharging and also performs controlled over
discharges.
👉Battery stores current electricity that produces from solar arrays for using when
sunlight is not visible, nighttime or other purposes.
👉Inverter is a critical component of any solar PV system that converts DC power
output of solar arrays into AC for AC appliances.
👉Lightning protection prevents electrical equipment's from damages caused by
lightning or induction of high voltage surge. It is required for the large size and
critical solar PV systems, which include the efficient grounding.
APPLICATIONS OF SOLAR CELL:
APPLICATION OF PV SYSTEMS:
Solar PV power systems are categories into four classes.
👉Standalone
👉PV hybrid
👉Grid connected
👉Solar power satellite
SOLAR SYSTEM DESIGN:
👉Power (watts) = current (Amps) X voltage (volts)
👉Energy (kWh)=Power (kW) X Time (hours)
👉Voltage Drop (volts) = Current (amps) X Resistance (ohms)
👉Components size depending upon our requirement.
SOLAR CELL EFFICIENCY:
• The efficiency of a solar cell (sometimes known as the power
conversion efficiency, or PCE, and also often abbreviated η)
represents the ratio where the output electrical power at the
maximum power point on the IV curve is divided by the
incident light power – typically using a standard AM1.5G
simulated solar spectrum
The efficiency of a solar cell is determined as the fraction of incident power
which is converted to electricity and is defined as:
Pmax= Voc Isc FF η = Voc Isc FF/Pinc
👉where Voc is the open-circuit voltage
👉where Isc is the short-circuit current
👉where FF is the fill factor
👉where η is the efficiency
RAPS APPLICATIONS:
Raps means remote area photovoltaic system
















Comments
Post a Comment